Isa Slots Definicion
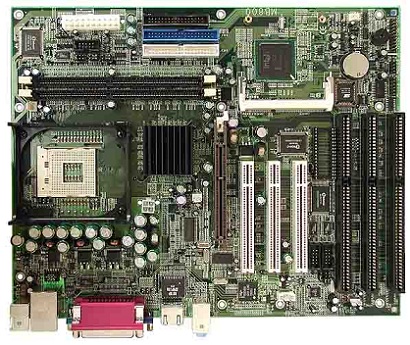
ISA: The most ancient type of expansion slot is the ISA, which stands for (get this) Industry Standard Architecture. That’s because it never really had a name until another, better type of expansion slot came along. ISA slots hang around to be compatible with older expansion cards. Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088 -based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles. ISA Slot Computer The ISA slot was the expansion method used for years. Today, PCIe rules the Market. For those who need to keep an old system running we have several offerings that should keep you running for some time to come. An ISA slot is “Industry Standard Architecture” which is the same old IBM cloned architecture we’ve known for years. It allows for expansion cards, video cards, network cards and extra serial port cards.

Isa Slots Definicion Para
Stands for 'Industry Standard Architecture.' ISA is a type of bus used in PCs for adding expansion cards. For example, an ISA slot may be used to add a video card, a network card, or an extra serial port. The original 8-bit version of PCI uses a 62 pin connection and supports clock speeds of 8 and 33 MHz. 16-bit PCI uses 98 pins and supports the same clock speeds.
Isa Slot Definition
The original 8-bit version of ISA was introduced in 1981 but the technology did not become widely used until 1984, when the 16-bit version was released. Two competing technologies -- MCA and VLB -- were also used by some manufacturers, but ISA remained the most common expansion bus for most of the 1980s and 1990s. However, by the end of the twentieth century, ISA ports were beginning to be replaced by faster PCI and AGP slots. Today, most computers only support PCI and AGP expansion cards.